As one of the largest private enterprises in Hubei, Wuhan Modern Group and its listed companies constituted the “Modern Department” with a reputation for being good at capital operation and continuous mergers and acquisitions. However, the “buy out” contemporary department is also under the enormous pressure of high goodwill and debts caused by a large number of mergers and acquisitions activities. Under the impact of the epidemic last year, the financial pressure faced by the contemporary department has further increased. At the same time, the contemporary department also began to continuously sell its assets and implement refinancing measures. In this context, the news that Guo Xudong, the former “first sister of the Issuing Examination Committee”, has been officially appointed as the vice chairman of Contemporary Group seems to be even more unusual.
On April 11, some media reported that Guo Xudong, the former “first sister of the China Securities Regulatory Commission”, had officially joined Wuhan Modern Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Modern Group), one of the largest private enterprises in Hubei, and served as the vice chairman of the board. .
Prior to this, Guo Xudong served in the China Securities Regulatory Commission for 21 years, and was in charge of the IPO issuance review work in the Issuance Department for many years, and served as a five-term issuance review committee. In August 2019, Guo Xudong was revealed to have submitted his resignation to the Securities Regulatory Commission. Since the identity of the supervisory cadre is more sensitive, Guo Xudong’s whereabouts have been confusing. However, in September last year, a report on the official website of Contemporary Group Sun Company accidentally revealed Guo Xudong’s next stop.
The joining of Guo Xudong also makes Contemporary Group and founder Ai Luming become the focus of market attention. Accompanied by arduous entrepreneurship and dazzling capital operations, Dangdai Group started from a small research institute established in 1988 with a start-up capital of 2,000 yuan, and finally grew into one of the largest private enterprises in Hubei with multiple listed companies and 100 billion assets. One. However, cross-industry operations and a large number of mergers and acquisitions activities have also made Modern Group’s goodwill and debt high, and internal troubles are deeply hidden. Now that Guo Xudong’s arrival can help Contemporary Group to eliminate financial “hidden worries”, perhaps it is particularly worthy of attention.
In the past, the “first sister of the trial” joined the contemporary group
Guo Xudong is no stranger to many listed companies. According to public information, Guo Xudong served as a member of the 9th, 10th, 11th, 17th, and 18th issuance review committees, and he can be described as a “five dynasty veteran.”
In 2007, Guo Xudong’s name appeared for the first time on the list of the Issuance Examination Committee of the China Securities Regulatory Commission as a part-time member, and was re-elected as a part-time member of the Issuance Examination Committee in 2008 and 2009. In 2010, Guo Xudong temporarily left the front line of IPO review, and has since served as Deputy Inspector and Deputy Director of the Non-listed Public Companies Department of the China Securities Regulatory Commission and Deputy Director of the Public Companies Department of the China Securities Regulatory Commission. After seven years away from the front-line issuance review work, Guo Xudong returned to the issuance review committee again in September 2017. At this time, her position was the deputy director of the issuance supervision department of the China Securities Regulatory Commission and ranked first on the list of the issuance review committee. Because of its professional skills and strict requirements on investment banking business, it is known by the market as the “iron-clad issuance review committee” and the “IPO gatekeeper”.
However, in early August 2019, it was reported that Guo Xudong had formally submitted his resignation to the Securities Regulatory Commission and was approved in September of the same year. However, it was not until July 2020 that the China Securities Regulatory Commission officially released an announcement to remove Guo Xudong as a member of the 18th Issuance Examination Committee.
Due to the sensitive identity of the supervisory cadres, Guo Xudong’s whereabouts after leaving his post has attracted much attention from the market, but it has always been an unsolved mystery. During this period, there were many rumors that it would accept the invitation of the brokerage company to “go into the sea”, but to no avail. It was not until September last year that Guo Xudong’s next stop was revealed in a news report by a Sun company under the Modern Group.
On September 11, 2020, the official website of Yichang Sanxia Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. published a report titled “Leaders of Contemporary Group and Renfu Pharmaceutical Group Investigating Neomycin Sulfate Industrial Base”, which mentioned On August 18, Guo Xudong, Vice Chairman of Contemporary Group, and other senior executives went to the company’s factory for investigation. It is reported that Sanxia Pharmaceutical is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Renfu Pharmaceutical, a subsidiary of Modern Group. According to recent media verification, Guo Xudong in the news report is the former “first sister of the Issuing Examination Committee” Guo Xudong. However, the above report has been taken down by it.
What’s interesting is that, unlike the previous regulatory officials who usually went to the sea to devote themselves to financial institutions such as securities firms and funds, Guo Xudong’s choice seemed a bit “alternative.” Some analysts said that this may be due to its three-year “circumvention period” transitional arrangement, and other arrangements may be made once the “circumvention period” has passed.
“Buy Out” Wuhan Contemporary Department
Regardless of whether Guo Xudong’s joining is a temporary act or a long-term act, this has undoubtedly made Contemporary Group the focus of market attention.
As one of the largest private enterprises in Hubei, Contemporary Group is strong. According to the 2020 Hubei Top 100 Private Enterprises List released by the Hubei Federation of Industry and Commerce in October last year, according to the 2019 revenue ranking, Contemporary Group ranked ninth in Hubei Province. According to the official website of Modern Group, as of September 30, 2020, the total assets of the group have exceeded 100 billion yuan.
Behind the hundreds of billions of assets is the dazzling capital operation of Contemporary Group. To a certain extent, the development of Contemporary Group can be said to be a history of mergers and acquisitions.
In 1988, the founder Ai Luming and six Wuhan University alumni registered and established the Institute of Contemporary Biochemical Technology in Hongshan District, Wuhan with 2,000 yuan. The main business is to extract urokinase from urine and export it to Japan. This is also regarded as Ai Luming and his The starting point for the fortune of Wuhan Modern Group.
In 1993, Ai Luming and others established Wuhan Contemporary Technology High-tech Industry Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as “Contemporary Technology”). Four years later, Modern Technology successfully landed on the capital market. This is today’s “Human Welfare Medicine”, and it is also the first listed company under the Modern Group.
After accumulating a certain amount of capital in the medical field, the contemporary group began to expand its territory through various capital operations, and gradually accelerated its deployment in the textile, real estate, tourism, cultural and sports, financial and other fields, and a huge “contemporary” empire in Wuhan is about to emerge.
In 2010, Modern Group spent 900 million yuan to bid for a 36.77% stake in Anhui Huamao Group, and indirectly held shares in its listed company Huamao, and entered the textile industry.
In the same year, Dangdai Group held 5.818 million shares of Sante Ropeway through the transfer of Wuhan Optics Valley Ventures, becoming the third largest shareholder of Sante Ropeway and stepping into the tourism industry. In 2013, Dangdai Group increased its shareholding ratio from 4.85% to 10.5% through participation in Sante Ropeway, second only to 11.71% of the largest shareholder, and only one step away from holding Sante Ropeway. Unexpectedly, a “Cheng Yaojin” came out halfway, and then the three special ropeway was raised by Meng Kai, the actual controller of the situation in Hunan and Hubei. After fierce competition, contemporary technology finally won. At the end of 2013, Modern Technology increased its shareholding by subsequent increase, and its total shareholding ratio with those acting in concert rose to 14.82%, becoming the largest shareholder, and finally taking the controlling stake in Sante Ropeway.
In May 2015, Dangdai Group signed a capital increase agreement with Xinxing Hanyi, the largest shareholder of Daobo Co., Ltd. (renamed Dangdai Mingcheng in May of the following year, now Dangdai Style), and Dangdai Group invested 300 million yuan to subscribe for the new registration of Xinxing Hanyi Capital. After the capital increase is completed, Dangdai Group becomes the controlling shareholder of Daobo Co., Ltd. to deploy the cultural and sports industry. In addition, Modern Group also indirectly holds shares of Tianfeng Securities through Renfu Medicine, and it is involved in the financial industry.
In fact, the above is just the tip of the iceberg of contemporary group investment and merger cases. According to the company’s data, the number of companies directly controlled by Contemporary Group is as many as 609, and the number of companies indirectly holding shares is as high as 1,000.
Under hidden worries, refinancing frantically “tonic blood”
Modern Group, which operates and manages many subsidiaries across industries, also has internal worries. The impairment of goodwill caused by a large number of mergers and acquisitions in the past few years has been the first to bear the brunt.
Take Renfu Medicine, the core asset of Contemporary Group, as an example. In 2018, the company had a net loss of 386 million yuan due to a provision of 3.561 billion yuan in asset impairment losses. As of the end of the third quarter of 2020, Renfu Pharmaceutical still has 3.408 billion yuan in goodwill, which is more than three times the net profit of 1.044 billion yuan in the first three quarters of last year.
At the group level, as of the end of the third quarter of 2020, The scale of Goodwill of Modern Group dropped by nearly half compared with the same period of the previous year, but still 4.171 billion yuan, accounting for 8.95% of non-current assets, more than three times the net profit of 1.213 billion yuan in the first three quarters of last year, facing a larger business Reputation impairment risk.
In addition to the high reputation of goodwill, the debt problem of the contemporary group has also been criticized. As of the end of the third quarter of 2020, Modern Group’s total assets were 100.329 billion yuan, total liabilities were 68.186 billion yuan, and the asset-liability ratio was 67.96%, an increase of 2.21 percentage points from the same period last year. The core asset Renfu Medicine also has a heavy debt burden, and the debt-to-asset ratio continues to rise. As of the end of the third quarter of last year, Renfu Pharmaceutical’s total liabilities reached 24.95 billion yuan, exceeding the annual figures for 2018 and 2019, and the debt-to-asset ratio further rose to 71.4%.
At the same time, the poor performance has cast a shadow over Renfu Pharmaceutical’s reduction of its asset-liability ratio. In the first three quarters of 2020, the company achieved operating income of 14.8 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 7.81%; net profits attributable to shareholders of listed companies were 613 million yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 17.83%.
It is worth noting that as of March 10 this year, Renfu Pharmaceutical’s controlling shareholder, Modern Group pledged approximately 388 million shares, accounting for 79.93% of the total number of shares in the company. Nearly 80% of the holdings of the controlling shareholder have been pledged, which shows that the company’s use of funds is relatively tight.
In addition, the performance of several other listed companies under the contemporary group is also lackluster. In 2020, the revenue of Sante Ropeway plummeted by more than 40% year-on-year. Due to the transfer of the equity of 5 participating and holding companies during the reporting period, the company’s net profit surged 150% last year, but after deducting non-recurring gains and losses, it was at a loss, with a net loss of 160 million yuan. Another listed company, Contemporary Style and Sports, turned profits into losses last year, with an estimated net loss of 1.55 billion to 1.95 billion yuan.
In this context, in recent years, Human Welfare and Pharmaceuticals has continuously stripped off non-core assets, accelerated the withdrawal of funds, and optimized the asset structure. The contemporary department’s demand for “blood supplementation” through refinancing activities has become more urgent. Therefore, for the refinancing and other capital operations of contemporary listed companies, the joining of Guo Xudong, who has rich contacts and professional experience, appears to be “just in time” and has a different meaning.
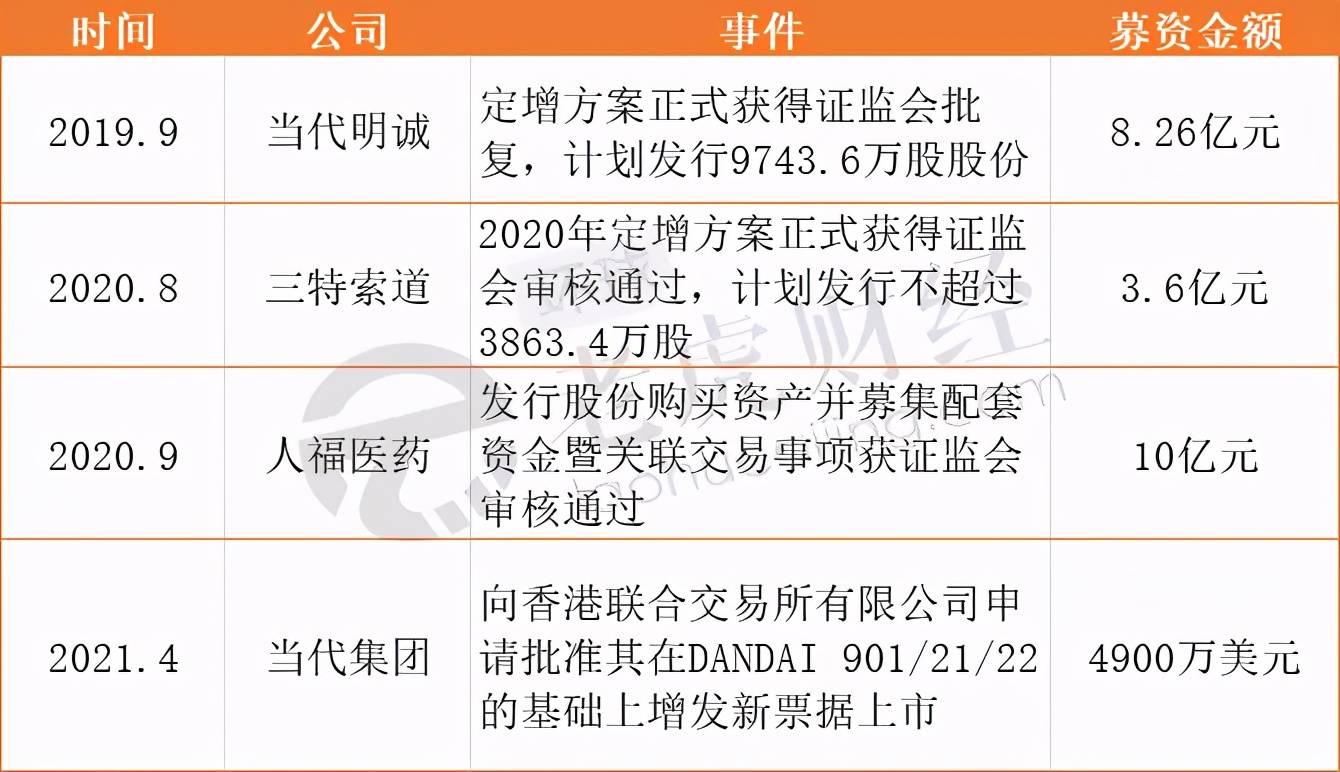
According to incomplete statistics, in the past year or so, before and after Guo Xudong joined the Modern Group, Modern Group and its listed companies have conducted at least four refinancing activities, raising a total of more than 2.5 billion yuan.





























































You must log in to post a comment.