By mid-to-late June, three Chinese astronauts had entered the “Tiangong” space station on the Shenzhou XII spacecraft and began preliminary operations. Faced with the situation where the former is on track, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which is eager to launch a manned lunar exploration program and multiple deep-space projects in 2024, but suffers from a limited budget, seems to have found the code of wealth.
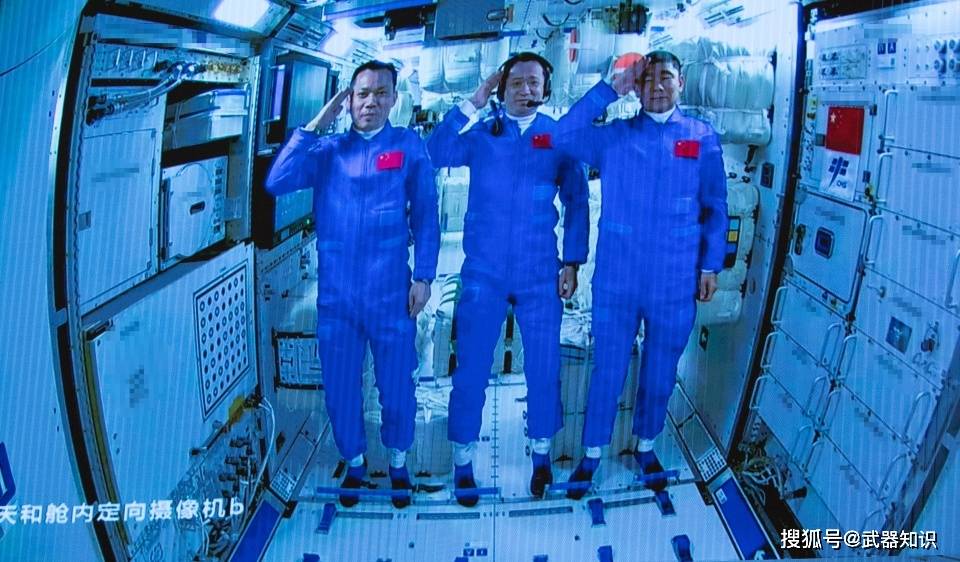

As of June 18th, a group of professionals led by NASA Administrator Nielsen began to make a big splash on June 18th, emphasizing that the United States must always “watch China”. Therefore, the Biden administration needs to allocate more funds to NASA. The Western world has also set off a wave of “China challenging the U.S. space dominance.”
For a time, from Beijing to Washington were passively involved in a space race. Few people thought that outside of China and the United States, there would be a third challenger in low-Earth orbit. It was when it confirmed the China-Russia joint moon landing plan, and at the same time announced that it would launch the “National Orbital Space Station” project in Russia in 2025. The space game between China, the United States and Russia has thus entered an accelerated phase.
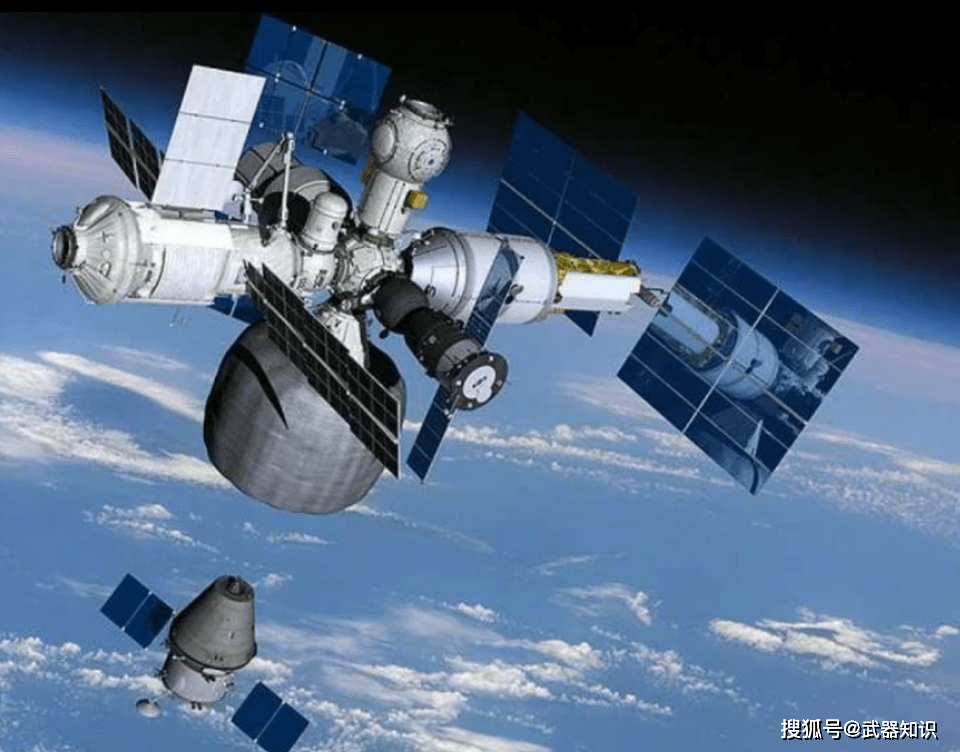
Also on June 11th, Rogozin, President of the Russian Aerospace Corporation, clearly talked about the future plan of ROSS in an interview with the country’s largest-circulation tabloid “Komsomolskaya Pravda”.
Rogozin pointed out in a straightforward manner that although Russia will still launch the “Science” capsule for the International Space Station (ISS) as planned on July 15th, to ensure that the ISS can still operate as planned until its retirement in 2030. But Russia will also end its cooperative relationship with ISS after 2026 and begin to build its “replaceable parts” space station, and launch its first core module in 2025. RIA Novosti also pointed out in a report on the 11th that Russia plans to build a “modular” low-orbit, multi-functional space station.

In fact, the Russian Aerospace Corporation’s space station plan will have some clues in February 2021. After Rogozin reported his work plan to Russian President Putin on February 11, Putin emphasized on the same day that Russia should continue to advance the manned space project in a rhythmic manner. Since this instruction was issued almost at the same time as the memorandum on the Sino-Russian lunar research station project approved by Russian Prime Minister Mishustin on February 12, the outside world once thought that the limited-funded Russian manned space project might become the future Sino-Russian project. Part of the joint moon landing project.
However, as Russia announced its withdrawal from the International Space Station on April 18, 2021, and began to display its “Diamond 2” core cabin and other equipment preserved before the disintegration of the Soviet Union, the outside world discovered that Russia, which has an independent technical foundation, did not originally Satisfied with OEM space station facilities for the United States and assisting in the transportation of astronauts, Russian astronauts and decision-makers who still have memories of the Soviet era are brewing big moves.

The ISS project, launched in 1998, has become a symbol of humiliation in the Russian aerospace industry. Because one of the cores of the ISS, the “Star” functional module was originally the core of the “Peace 2” space station during the Soviet era. After the construction of the project was completed in 1985, after the disintegration of the Soviet Union, it was revised to the “Peace 1.5” program, which was used as a plan to extend the service life of the “Mir” space station. It was later modified in 1992 to include 5 space capsules. Peace 2″ plan.
However, as the United States abandoned its “Freedom” space program after 1990 and switched to purchasing and receiving Russian space supplies, after the disintegration, the Russian authorities quickly abandoned the “Peace 2” plan due to the economic situation. Russia originally planned The design for the “Peace 2” was finally integrated into the ISS.

At present, in the face of the fact that the United States owns 11 of the 15 module capsules of the ISS, Russia only owns 4 of them. After years of debate, Russia finally chose not to continue to contribute more to the US-led ISS. power. As Russia gradually determined a simple plan including core cabins, dedicated production cabins, logistics and logistics cabins, platform cabins, and commercial cabins after October 2020, the Russian Aerospace Corporation restarted the “Peaceful” program, including the “Diamond 2”. After the space capsule equipment based on the No. 2 program, the development and operation of the ROSS station became possible.
In a sense, the operation of the ROSS station may also be an important occasion for Russia to declare its space capabilities to China, the United States and European parties. When Rogozin announced at the recent space summit that Russia is discussing with France to transform the Guyana Space Center so that it can be used for manned space missions, Russia’s actions against the European Union also showed a reality, that is, low Earth orbit in the 21st century. Not only can it accommodate China and the United States, it may also accommodate Russia.




























































You must log in to post a comment.