Source: Zhong Zhengsheng Economic Analysis
Authors: Zhong Zhengsheng, Zhang Lu, Fan Chengkai (Zhong Zhengsheng is a director of the China Chief Economist Forum, the chief economist of Ping An Securities, and the director of the research institute)

1. The U.S. CPI increased sharply year-on-year but slowed down month-on-month. The year-on-year readings of the US CPI indicator in May continued to hit new highs, but the growth rate of most of the sub-items decreased, which may make the market more agree with the “temporary inflation theory.” The second-hand car and truck index rose 7.3% month-on-month, slower than the previous value of 10%, but still maintained a high growth rate, continuing to contribute one-third of the growth of all projects. We believe that there are more reasons to believe that the rise in US prices has a certain degree of “stickiness”, especially in the second half of 2021, as the service industry demand is further restored, the adjustment of the supply side may not be timely. We will increase the CPI growth rate in the next period of time to 0.2%. Under the baseline scenario, the CPI in June may reach 4.6% year-on-year, and the CPI for the whole year of 2021 may reach 4.1% year-on-year. The significant drop in CPI year-on-year growth may not be seen until after the second quarter of 2022.
2. The prospects for the recovery of the US job market are relatively optimistic. U.S. employment data released in the past week showed that the number of job vacancies reached a record high of 9.286 million, and the job vacancy rate reached 6%, which is much higher than the level of about 4.5% before the epidemic. This shows that labor demand continues to recover and the job market continues to be actively matched. process. On the other hand, as half of the states in the United States will suspend the extra $300 weekly unemployment benefits in advance from June to July, residents’ demand for finding jobs has risen, which is reflected in the continued decline in the number of initial jobless claims. In the future, as “herd immunity” approaches, the alleviation of the epidemic will allow the catering, leisure and tourism industries to open up more comprehensively, and at the same time alleviate residents’ worries about employment risks.
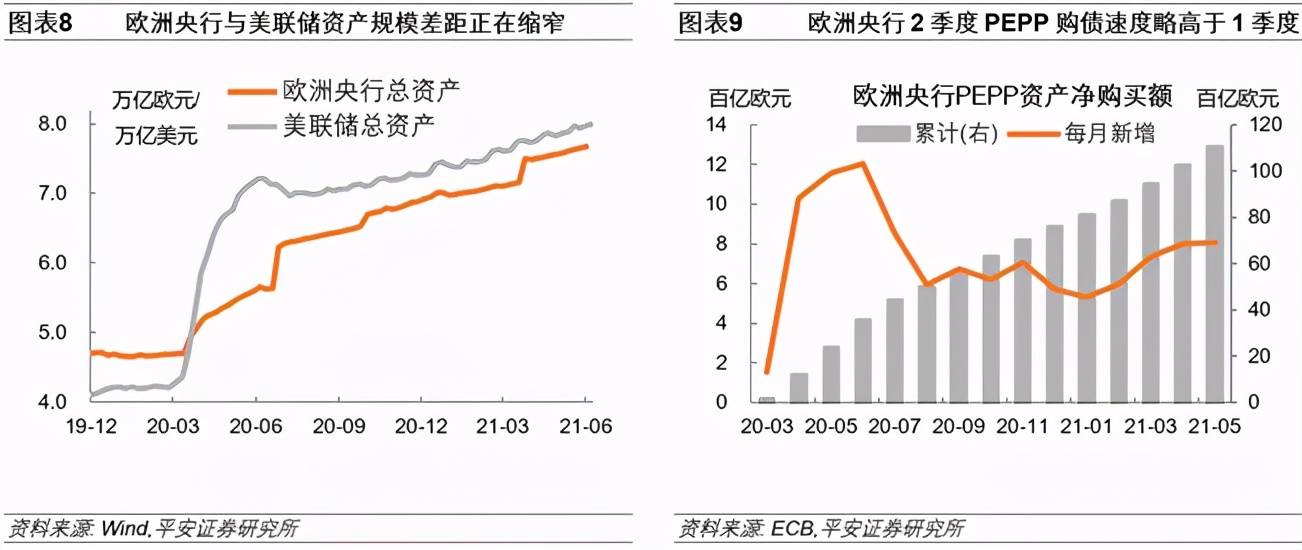
3. The European Central Bank intends to significantly accelerate the pace of PEPP bond purchases. The European Central Bank announced its June interest rate resolution, maintaining the three key interest rates unchanged, and promised to significantly accelerate the purchase of the Emergency Anti-epidemic Bond Purchase Program (PEPP) from June to September, reiterating that PEPP will last at least until the end of March 2022. And maintain the total size of 1.85 trillion euros unchanged. In comparison, the asset gap between the European Central Bank and the Fed has narrowed significantly since April. In the future, the pace of PEPP bond purchases will continue to accelerate, and there may be devaluation pressure on the euro against the dollar. At the same time, the European Central Bank raised the Eurozone GDP growth rate and CPI index forecasts for 2021-2022. It is estimated that Eurozone GDP will grow by 4.6% in 2021, compared to the previous forecast of 4%; the Eurozone CPI is expected to be 1.9% in 2021, compared to the previous forecast of 1.5. %. European Central Bank President Lagarde’s overall speech was partial, emphasizing that premature tightening of monetary and fiscal stimulus would pose risks to economic growth and inflation. He said that upward pressure on inflation in the second half of 2021 will be limited, but the temporary factors behind inflation are somewhat different. Uplift.
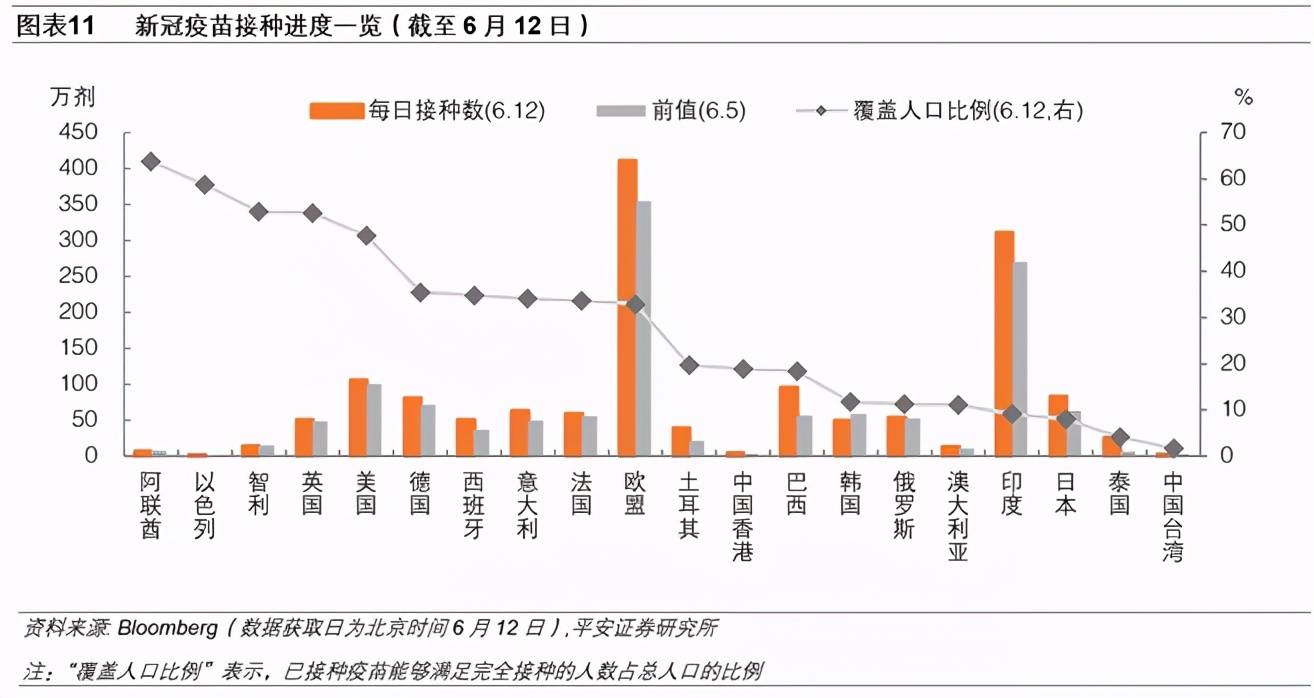
4. Overseas epidemic situation and vaccine tracking: The Asian epidemic situation has begun to ease gradually. The number of new cases in Taiwan, China has dropped, and the number of new cases per day has fallen to less than 300; the number of new cases in a single day in India has fallen below 100,000 for 5 consecutive days, and the “risk” entered the “unblocking 1.0” stage on June 7 . In terms of vaccines, the European Union and India rank second and third in the world in terms of vaccination rates. The vaccination rate in the United States is not faster than before, and the new vaccination goals of the Biden administration may be difficult to complete on time.
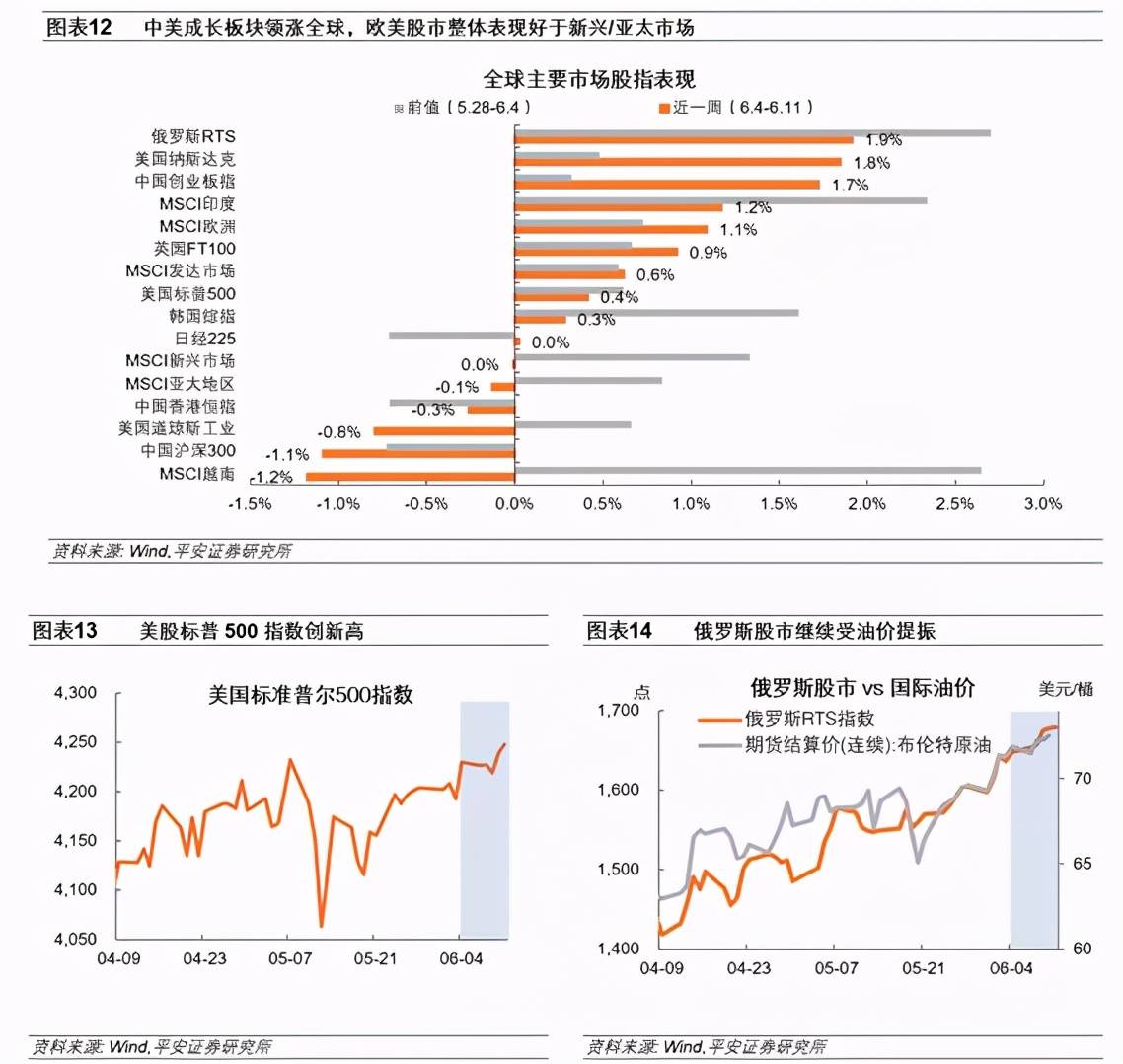
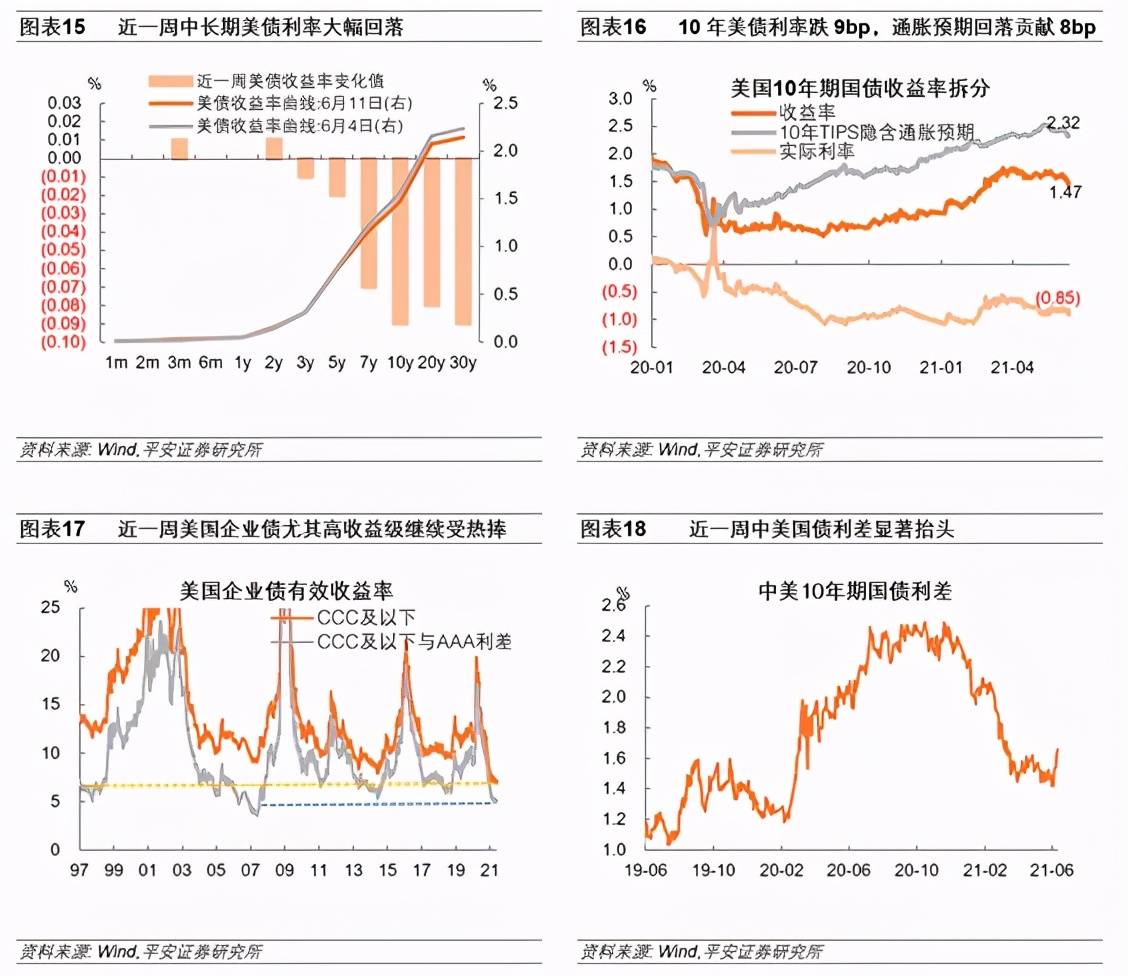
5. Global asset performance: Global stock markets-the Sino-US growth sector led the world, and the S&P 500 reached a new high. The recent fall in market inflation expectations has alleviated concerns about “killing valuations”, and global risk appetite remains high. On the other hand, the value sectors of China and the U.S. fluctuate. The MSCI Europe Index rose 1.1%, outperforming MSCI Emerging Markets (down 0.0%) and Asia Pacific (down 0.1%). Global bond market-10-year U.S. bond interest rates fell below 1.5% for the first time since March 3. It closed at 1.47% on June 11. The fall in inflation expectations is the key driver. In the 10-year US bond interest rate drop of 9bp, the fall in inflation expectations contributed 8bp. In addition, abundant funds in the US market have also increased the demand for US debt to a certain extent. US high-yield corporate bonds continue to be sought after. China-US bond spreads have risen significantly. Commodity market-crude oil prices have continued to rise in the past week, WTI crude oil futures prices rose, closing at US$70.91 per barrel on June 11. Although the WTI crude oil inventory level has dropped significantly recently, it is still 20-30 million barrels higher than the pre-epidemic level. The OPEC report is more optimistic about global crude oil demand. Foreign exchange market-the dollar index jumped from 90.05 to 90.51 on June 11, It exceeds 90.50 on June 3, which is a new high since May 13. It should be noted that the rebound of the U.S. dollar is not due to the market’s early expectations of Taper or interest rate hikes, but more from the expectation of the European Central Bank’s expansion and acceleration of the balance sheet. The Fed’s pace of table expansion and the timing of Taper are likely to be earlier than the European Central Bank. In addition, the recent decline in initial unemployment claims and the fall in inflation expectations may also marginally increase market confidence in the U.S. economy.
1. Overseas key tracking
1. U.S. economy: U.S. CPI increased year-on-year but slowed down month-on-month
The U.S. CPI indicator reading in May continued to reach new highs, but most of the sub-items declined compared to April, which may make the market more agree with the “temporary inflation theory.” US May CPI rose 5.0% year-on-year, the highest growth rate since August 2008; core CPI rose 3.8% year-on-year, the growth rate hit a new high since 1992. Looking at the sub-item, the total CPI index rose by 0.6% month-on-month. Although it was slower than the previous value of 0.8%, it still significantly exceeded the 2016-2019 average of 0.18%. The core CPI rose 0.7% month-on-month, from the previous value of 0.9%. The month-on-month increase in most CPI items in May did not exceed that in April. Among them, the second-hand car and truck index rose by 7.3% month-on-month, which was slower than the previous value by 10%, but still maintained a relatively high growth rate, continuing to contribute to the growth of all projects. One part. In May, the new car index rose 1.6% month-on-month, the largest monthly increase since October 2009; the apparel sub-item rose 1.2% month-on-month, significantly exceeding the previous value of 0.3%.
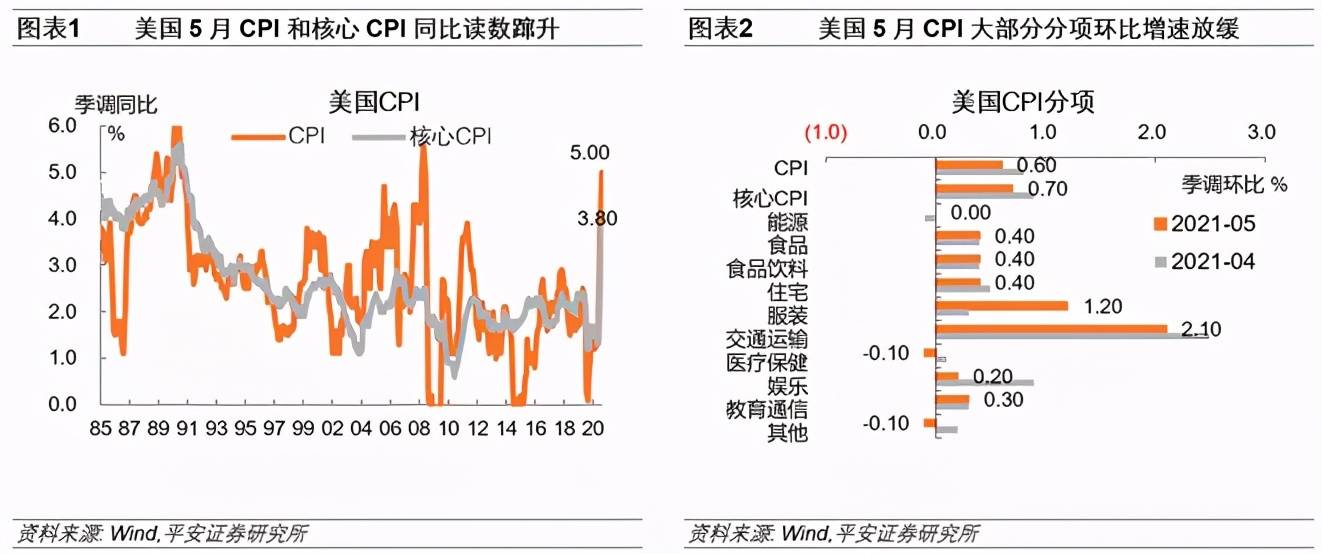
The CPI in May was still higher than market expectations and we calculated it on the basis of the monthly average month-on-month (0.18%) from 2016 to 2019.We believe that there are now more reasons to believe that rising prices in the United States have a certain degree of “stickiness”, especially in In the second half of 2021, as demand in the service industry is further restored, the adjustment on the supply side may not be timely. We will increase the CPI growth rate to 0.2% in the next period of time. Under the baseline scenario, the CPI in June may reach 4.6% year-on-year, and the CPI for the whole year of 2021 may reach 4.1% year-on-year. The significant drop in CPI year-on-year growth may not be seen until after the second quarter of 2022.
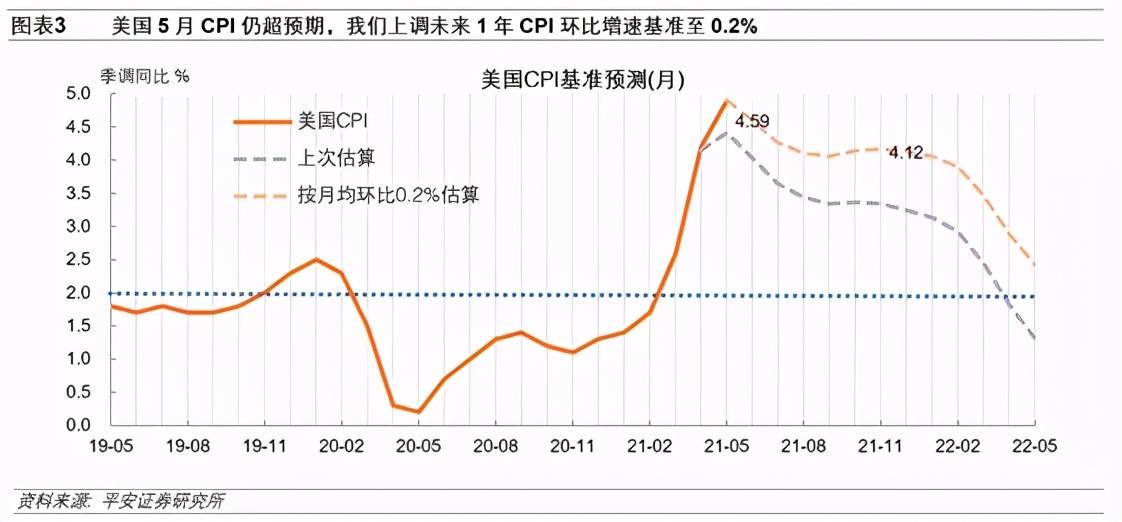
The US employment data released in the past week showed that the number of job vacancies reached a record high of 9.286 million, and the job vacancy rate reached 6%, which is much higher than the level of about 4.5% before the epidemic. This shows that the demand for labor continues to recover, which means that the job market continues to be active. The matching process. On the other hand, as half of the states in the United States will suspend the extra $300 weekly unemployment benefit in advance from June to July (the other half of the states will expire in early September), the demand for jobs from residents has risen recently. This is reflected in The number of initial jobless claims continues to decline. In the future, as “herd immunity” approaches, the alleviation of the epidemic will allow the catering, leisure and tourism industries to open up more comprehensively, and at the same time alleviate residents’ worries about employment risks. Overall, we believe that the prospects for the recovery of the US job market are more optimistic.
The results of the April Job Vacancies and Labor Flow Survey (JOLTS) released by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics on June 8 showed that the number of job vacancies in April exceeded the 9 million mark, reaching a record high of 9.286 million. The number of independent resignations in April was 3.985 million, a record high. The number of unemployed persons in April was only 526,000 more than the number of vacancies, down from 1.4 million in March. The employment rate in April was 4.2%, the same as in March.
As of the week of June 5, the number of initial applications for unemployment benefits in the United States fell to 376,000, the previous value of 385,000, maintaining a decline for 7 consecutive weeks. As of the week of May 29, the number of continued jobless claims dropped from 3.757 million to 3.499 million, but it was still twice the level before the epidemic.
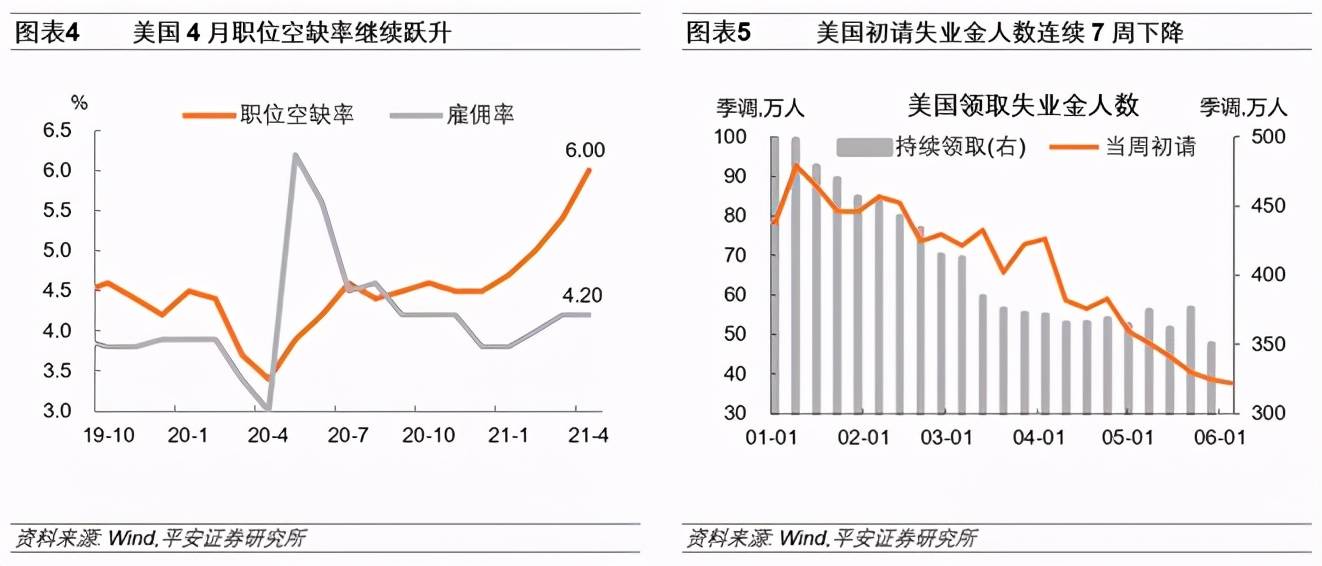
US consumer confidence and expectations continue to improve. The Consumer Confidence Index of the University of Michigan in the United States was 86.4 at the beginning of June, which was higher than the expected value of 84.4, and was significantly higher than the final value of 82.9 in May. We observe the difference between the consumer expectations index and the status quo index. The figure in June was -6.8, which is the third time it has risen above -10 since April 2020 and October 2020. As the “herd immunity” approaches and The job market has recovered, and American consumers’ expectations for the future have improved significantly.
In the past week, the number of Fed’s overnight reverse repurchases continued to climb and hit record highs continuously. On June 11, the overnight reverse repurchase of Treasury bills amounted to US$547.81 billion, which was US$2.57 trillion for the entire week and US$1.85 trillion the previous week. And the historical peak usually occurs at the end of the month, and the jump in this number at the beginning of June is really rare. Excess liquidity in the U.S. money market has continued to push down the overnight general secured repo (GC Repo) interest rate to close to 0%, which has triggered concerns about “negative interest rates” in the market. There is a view that at the upcoming June interest rate meeting, the Fed may slightly increase the reverse repo interest rate and excess reserve interest rate to control the demand for reverse repo.
2. European economy: The European Central Bank intends to significantly accelerate the pace of PEPP bond purchases
On June 10, the European Central Bank announced its June interest rate resolution, maintaining the three key interest rates unchanged (the main refinancing, deposit facility interest rates, and marginal lending rates are 0.00%, -0.50%, and 0.25%, respectively), in line with market expectations. The European Central Bank promised to significantly speed up the purchase of the Emergency Anti-epidemic Bond Purchase Program (PEPP) from June to September. “Significantly higher than the first quarter”, reiterating that PEPP will continue at least until the end of March 2022, and maintain the total size of 1.85 trillion euros unchanged; will continue to purchase debts of 20 billion euros per month in accordance with the Asset Purchase Plan (APP); will reinvest The maturity of PEPP bonds will last at least until the end of 2023. In comparison, the asset gap between the European Central Bank and the Federal Reserve has narrowed significantly since April. In the future, the pace of PEPP bond purchases will accelerate or further narrow the gap, and there may be devaluation pressure on the euro against the U.S. dollar.
At the same time, the European Central Bank also raised the euro zone GDP growth rate and CPI index forecast for 2021-2022. The GDP of the Eurozone is expected to grow by 4.6% in 2021, compared with the previous forecast of 4%; GDP growth in 2022 is expected to grow by 4.7%, which was previously expected to grow by 4.1%; the GDP growth forecast in 2023 is maintained unchanged at 2.1%.Expected In 2021, the Eurozone CPI is 1.9%, which was previously expected to be 1.5%; the CPI is expected to be 1.5% in 2022. Previously expected to be 1.2%; maintain the 2023 CPI forecast at 1.4% unchanged. The President of the European Central Bank, Lagarde, gave a partial speech. Emphasizing that premature tightening of monetary and fiscal stimulus will pose risks to economic growth and inflation, saying that inflation expectations will rise in the second half of 2021, but upward pressure is limited, and the temporary factors behind inflation have risen.
3. Overseas epidemic situation and vaccine tracking: Asian epidemic situation begins to ease gradually
The global epidemic has improved, As of June 11, a total of 176 million people have been diagnosed in the global new crown, and the cumulative global growth rate of confirmed diagnoses has fallen in the past week (1.5%, previous value 1.8%).
The epidemic in Asia has gradually eased, and the number of new cases in Taiwan has dropped. The daily increase in cases fell to less than 300. The cumulative increase in confirmed diagnoses in the past week was 19.2%, which was a significant decrease from the previous value of 36.9%. However, the daily number of new deaths in the past week was more than 20, and the mortality rate was much higher than the global average. Some experts worry that the decline in new diagnoses is related to the limited testing capabilities. The three Southeast Asian countries-Vietnam (20.4%, previous value 29.6%), Thailand (10.4%, previous value 18.6%) and Malaysia (7.2%, previous value 9.8%) have also seen an improvement in the cumulative increase in confirmed diagnoses.
India has entered the “Unblock 1.0” stage, This week, the cumulative increase in confirmed diagnoses fell to 2.3% (previous value 3.5%). The number of confirmed cases in India surpassed 100,000 for the first time in early April and continued to climb. The highest number was 410,000 in a single day. It has now fallen below 100,000 for 5 consecutive days. The Indian government has been impatient on June 7. Take risks” to carry out large-scale unblocking.

In terms of global vaccines, According to Bloomberg statistics, as of June 12, Beijing time, 178 countries around the world have received more than 2.3 billion doses of vaccine, and the global average daily dose exceeds 35.7 million doses.
In Europe, The EU’s cumulative vaccination volume is nearly 292 million doses, and the average daily vaccination volume in the past week has exceeded 4 million doses/day (previously 3.55 million doses/day). The vaccination rate is second only to mainland China in the world. The UK has vaccinated over 70 million doses, covering 52.6% of the population.
In the United States, At present, the United States has injected more than 300 million doses of vaccine, and 52% of people have received at least one dose, and the vaccination rate continues to maintain about 1 million doses per day. If the current vaccination rate is followed, the Biden administration’s vaccination target-70% of adults will receive at least one dose of the new crown vaccine before July 4-may not be completed on time.
In Asia, The daily vaccination in India exceeds 3 million doses (previously 2.71 million doses), a record high. Thailand has fully launched the new crown vaccination on June 7. Thailand has approved vaccines such as China’s Coxing and AstraZeneca, and will provide Thailand with 6 million doses of new crown vaccine in June. There is still no significant progress in the vaccination situation in Taiwan, China, which may restrict the prevention and control of the epidemic.
2. Global asset performance
1. Global stock markets-Sino-US growth sectors led global gains, S&P 500 hit a new high
In the past week (as of June 11), the US and China growth sectors led the world, with the Nasdaq and A-share ChiNext stocks rising 1.8% and 1.7% respectively. The U.S. S&P 500 index rose 0.4% for the entire week, closing at 4,239.18 and 4,247.44 on June 10 and 11, respectively, exceeding the record of 4,32.60 on May 7 and breaking a new record high. The recent fall in market inflation expectations has alleviated concerns about “killing valuations”, and global risk appetite remains high. On the other hand, both the Chinese and American value sectors fluctuated. The Dow Index and the A-share CSI 300 fell 0.8% and 1.1%, respectively. The MSCI Europe Index rose 1.1%, outperforming MSCI Emerging Markets (down 0.0%) and Asia Pacific (down 0.1%). Russia’s RTS (up 1.9%, previous value up 2.7%) has been continuously boosted by higher oil prices recently.
2. The global bond market-10-year U.S. bond yields fell below 1.5, and the fall in inflation expectations is the key driver
In the past week (as of June 11), interest rates on medium and long-term US bonds have fallen sharply, with 5-year, 7-year, 10-year and 30-year periods falling by 2bp, 7bp, 9bp and 9bp respectively. Among them, the 10-year U.S. bond interest rate fell below 1.5% for the first time since March 3, and closed at 1.45% and 1.47% on June 10 and 11, respectively. The fall in inflation expectations is the key driver to increase the demand for U.S. Treasuries. In the 9bp of the 10-year U.S. bond interest rate decline, the decline in inflation expectations contributed 8bp, and the fall in real interest rates only contributed 1bp. In addition, as shown by the Fed’s overnight reverse repurchase data, ample market funds have also increased the demand for U.S. debt to a certain extent.
In the past week (as of June 10), US corporate bonds (especially high-yield grades) continue to be sought after, The interest rate of AAA grade corporate bonds fell by 6bp, the BBB grade fell by 16bp, and the CCC grade and below fell by 22bp. This reflects the strong market preference of the bond market, and funds are actively seeking higher-yielding bond products. The 10-year China bond interest rate rose by 12.5bp. Against the background of falling U.S. interest rates, China-US bond spreads have risen significantly.
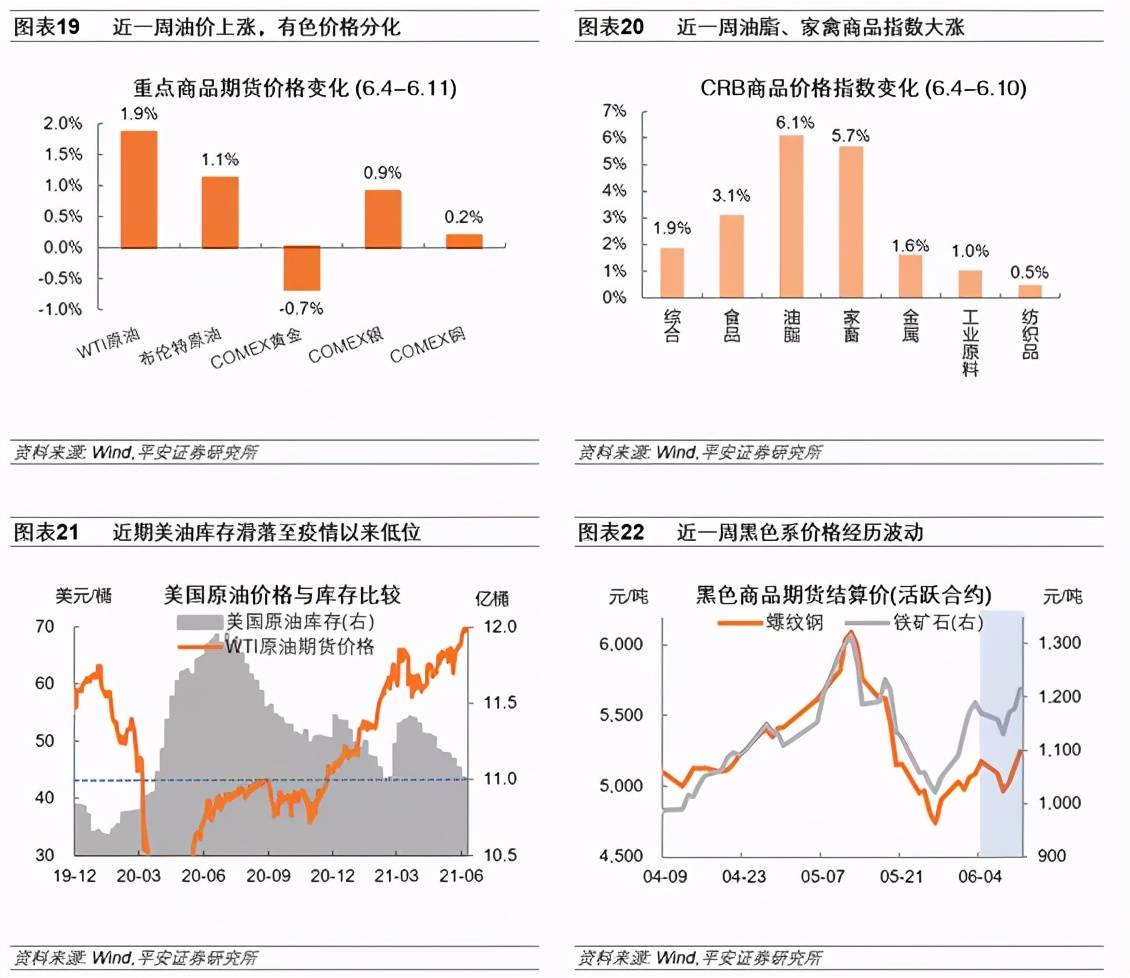
3. Commodity market-oil prices continue to rise, and prices of black products experience fluctuations
Crude oil prices continued to rise in the past week. WTI crude oil and Brent crude oil futures prices rose by 1.9% and 1.1% respectively. On June 11, the price per barrel closed at US$70.91 and US$72.69, respectively. The outlook for the global epidemic and vaccines continues to be clear, and oil-producing countries are more optimistic about global crude oil demand. The OPEC monthly report on June 10 showed that crude oil production in May was 25.463 million barrels per day, and in April it was 25.073 million barrels per day. OPEC still believes that oil demand will recover strongly in 2021. Based on the assumption that the world economy will grow by 5.5% in 2021 and the impact of the epidemic will be basically contained in the second half of the year, OPEC predicts that oil demand will increase by 5.95 million barrels per day this year, an increase of 6.6%. . It is estimated that the average daily demand for OPEC crude oil in the second half of 2021 will reach 29 million barrels, while the organization’s average daily output is only 25.46 million barrels. but, From the perspective of WTI crude oil inventory levels, although inventories have fallen significantly recently, close to the low level in late February this year (about 1.1 billion barrels), they are still 20-30 million barrels higher than the pre-epidemic level.
In terms of other commodities, COMEX gold fell 0.7%, silver rose 0.9%, and copper rose 0.2%. The prices of oil and poultry in the CRB commodity index rose sharply. Domestic black commodity futures prices experienced volatility, first falling and then rising. On June 11, the prices of rebar and iron ore per ton closed at 5,245 yuan and 1214.5 yuan, respectively, exceeding the rebound peak level on June 3.
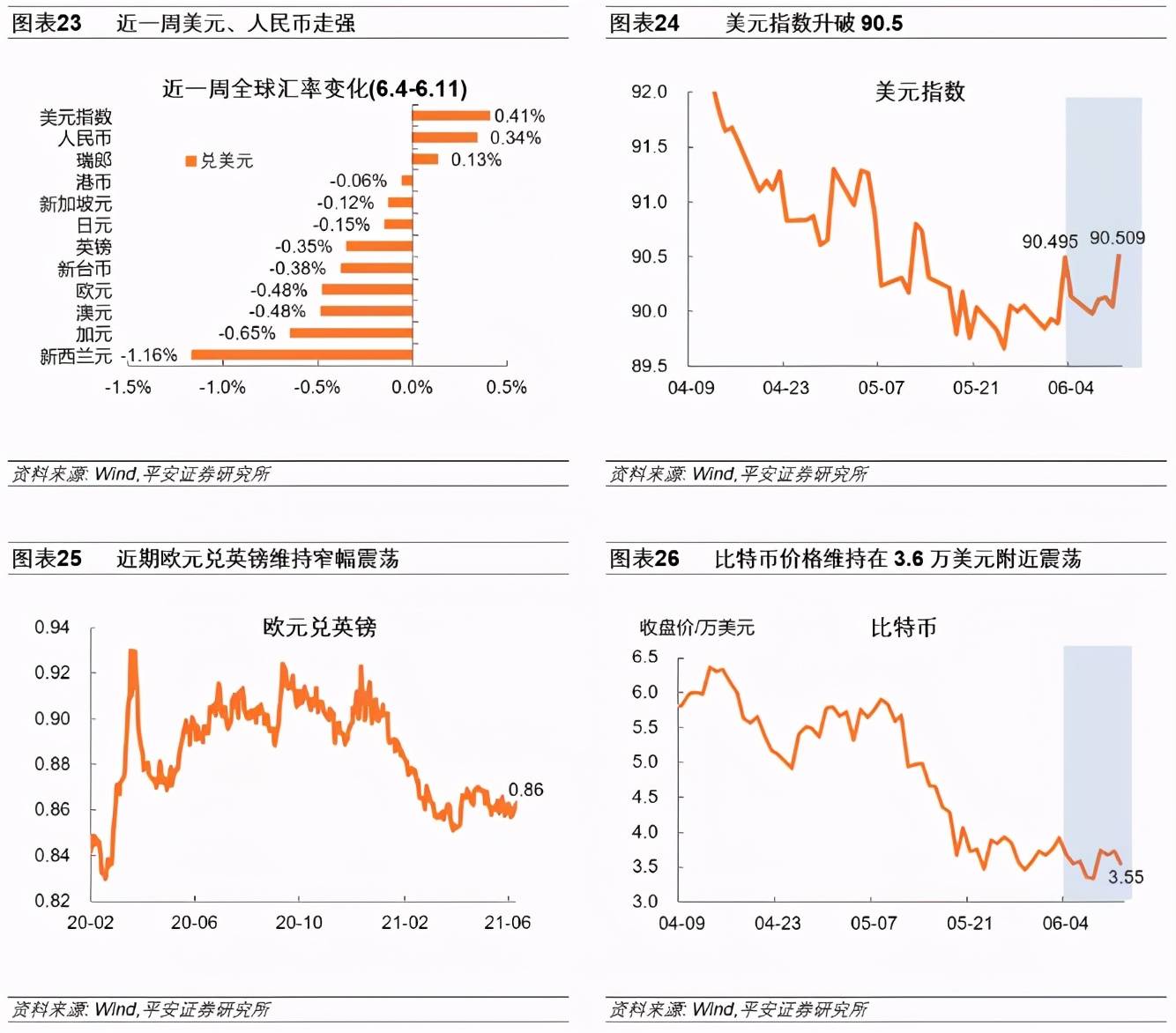
4. The foreign exchange market-the US dollar index rose above 90.5, and the renminbi strengthened against the US dollar “against the trend”
In the past week, the U.S. dollar index fell first and then rose. It jumped from 90.05 to 90.51 on June 11, exceeding 90.50 on June 3 and the highest since May 13. It should be noted that the rebound of the U.S. dollar is not due to the market’s early expectations of Taper or interest rate hikes, but more from the expectations of the European Central Bank’s expansion of the balance sheet. On June 10, the European Central Bank’s decision on interest rates meeting was a pigeon and announced that it will speed up bond purchases. The pace of table expansion and the timing of Taper are likely to be earlier than the European Central Bank. In addition, the recent decline in initial unemployment claims and the fall in inflation expectations may also marginally increase market confidence in the U.S. economy.
Against the backdrop of a strong US dollar, the yuan still rose 0.34% against the US dollar. Since February this year, the euro against the pound has been flat and has maintained a narrow range. The current price of the euro against the pound is still higher than the level before the epidemic. Since late May, the price of Bitcoin has fluctuated in the range of US$34,000 to US$40,000.
vv





























































You must log in to post a comment.