
The European Cup had just entered its second day, and the first round of Group B was surprised.
Danish player Eriksson suddenly fainted and fell to the ground
Heartbreaking…
Multiple topics are at the top of the hot search list

The scene shot, Eriksson seemed to roll his eyes and lose consciousness at the moment he fell to the ground.
After 13 minutes of full rescue, he finally managed to snatch the “Eros” Eriksen back from death!
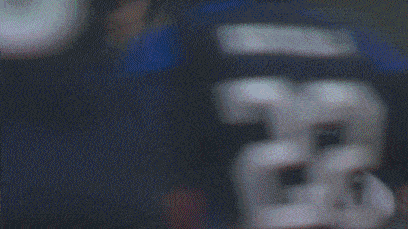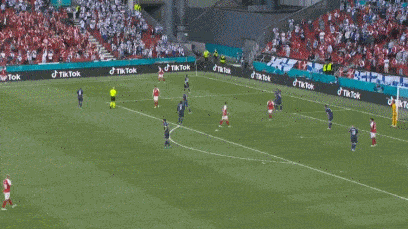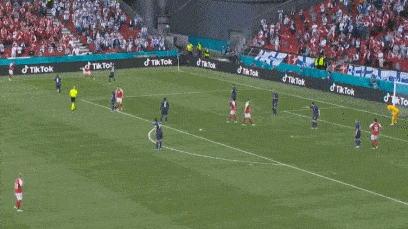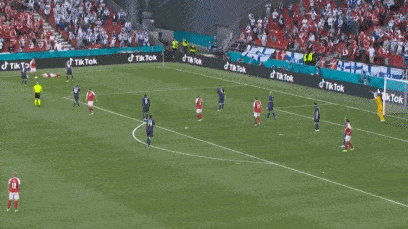 Erickson suddenly fell to the ground
Erickson suddenly fell to the ground
 Danish players form a circle to guard against leakage of privacy
Danish players form a circle to guard against leakage of privacy
At the European Cup, when Eriksson suddenly fell to the ground, the on-site medical staff staged a “speed of life and death” in a race against death. At this time, many people realized that sudden cardiac arrest, a sudden illness, is actually separated from everyone. Very close.
Everyone should master: cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Eriksson’s shocking scene made everyone once again focus on the invisible killer threatening human health—— Sudden cardiac death .
At present, the number of sudden deaths in our country ranks first in the world, and the only direct effect in the face of sudden death is Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) . Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a rescue operation performed immediately after a cardiac arrest. The golden resuscitation time is within 4 minutes. It is a life-saving technique for the heart and breathing of a sudden arrest, and is to restore the patient’s spontaneous breathing and spontaneous circulation.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation includes basic life support and advanced life support, which refers to a series of rescue measures to restore spontaneous circulation and even mentality in response to cardiac arrest in a timely, standardized and effective manner.
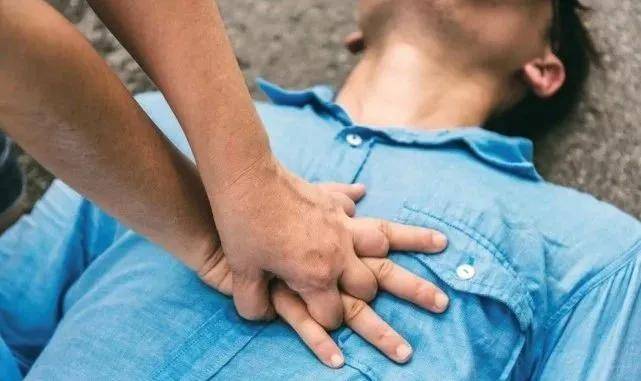
Among them, basic life support includes artificial circulation, unblocked respiratory tract, artificial respiration, and defibrillation.
1. Artificial circulation
“Artificial circulation” is an indispensable and important step in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. After a cardiac arrest, the human body’s engine heart stops working, and the “pump” cannot transport blood to the whole body. Through artificial circulation (chest compression), the chest cavity and heart are squeezed, just like we pinch a mineral water bottle. The blood inside is squeezed out and circulates throughout the body.
2. Smooth the airway
“Unblocked airway” refers to opening the airway (such as tilting the head back) so that the patient’s mouth and throat axis are in a straight line to prevent the tongue from blocking the airway opening, keep the airway open, and prepare for the next step of artificial respiration.
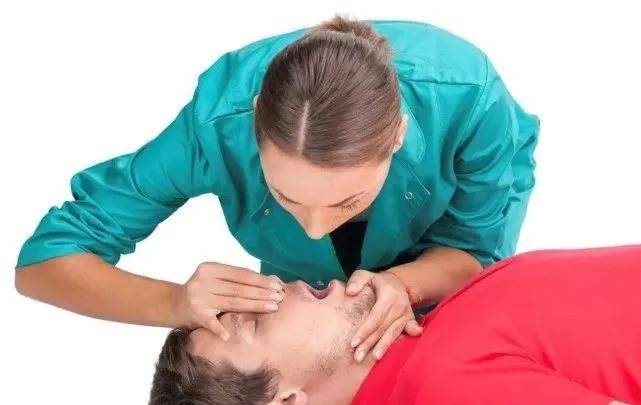
3. Artificial respiration
“Artificial respiration” can blow air from the mouth (or nose) into the lungs, temporarily alleviating the hypoxia in the body.

4. Defibrillation
“Defibrillation” is to eliminate the irregular “fibrillation state” of the heart. Generally, a defibrillator (AED) is used to quickly shock the patient’s heart to stop ventricular fibrillation.
Advanced life support is based on basic life support. Professional medical personnel use instruments and drugs to maintain the patient’s breathing and blood circulation.
It is worth mentioning that, The key to cardiopulmonary resuscitation is the start time of cardiopulmonary resuscitation . The earlier you start, the better the prognosis. Studies have shown that the survival rate of patients with cardiopulmonary resuscitation in less than 4 minutes can reach 43%~53%, and the survival rate is extremely low if it is greater than 10 minutes.
Therefore, for patients in cardiac arrest, Pay attention to the “golden 4 minutes” of the best rescue. The sooner the patient is given first aid, the greater the chance of saving lives.
Fortunately, Erickson has a group of partners and team doctors who know first aid knowledge. After the heart-wrenching 13-minute on-site rescue, he regained consciousness and came back to life.
Correct emergency rescue, keep these 5 points in mind
Whether it is for the family or the people around us, we should learn the knowledge of first aid for cardiac arrest and master the first aid skills within our capacity.
First of all, before performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation, it is necessary to determine whether the rescued person has a cardiac arrest.
1. Judge the reaction. You can tap and call out “What’s wrong with you” to see the patient’s response. If there is no response, go to the next step.
2. Determine breathing and pulse . You can judge whether you have breathing by directly observing the ups and downs of the thorax. The pulse is usually judged by touching the carotid artery. The method of judging the pulse is more professional, and it is best to receive formal training.
If the patient is found to be unresponsive and not breathing, the following first aid measures should be implemented immediately:
1. When you find that the patient is lying on the ground, you should Call the local emergency number immediately (120) , Ask for professional help.
2. After confirming that it is a cardiac arrest, start immediately High-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation , Strive for the best time for first aid.
Heart compressions outside the chest. The rescuer is on the right side of the patient and selects the lower half of the patient’s sternum as the compression point. Place the root of the left palm at the pressing point, press the root of the right palm on the back of the left hand, clasp the fingers tightly without touching the chest wall of the patient, straighten the arms, and press down with the root of the palm as the focus point without bending the elbow.
Note: The pressure should be appropriate. The compression frequency is 100~120 times/min, and the compression depth is not less than 5 cm but not more than 6 cm for adults. (Children are 1 cm to 2 cm). The trained rescuer is capable of artificial respiration and should be rescued according to the pressure: artificial respiration ratio of 30:2. Usually a rescue cycle is three rounds, that is, 90 compressions and 6 artificial respirations.
If there is a defibrillator on site, use the defibrillator as soon as possible after chest compressions.
3. Repeat chest compressions and artificial respiration alternately for rescue until the medical staff arrive at the scene or
Spontaneous breathing and pulse have been restored.
Here, it should be noted that chest compressions, artificial respiration and defibrillator use operation requirements are high, and professional training should be received in advance to improve the survival rate of rescued persons.
In the race between the gods of death and the god of love, it may be those minutes or even seconds that determine the final victory. If we can learn professional first aid knowledge and skills, we may save a life in the event of cardiac arrest.
Dr. Hu Zhen, expert reviewer of Daoyitong
Former Attending Physician of the Department of Internal Medicine of Chongqing Top 3 Hospital
references
[1]Wang Lixiang, Meng Qingyi, Yu Tao. 2016 China Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Expert Consensus[J].Chinese Critical Care Medicine, 2016, 28(12):1059-1079.
[2]Wang Xiaogang, Gao Ding. Clinical experience of 505 cases of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in patients with prehospital cardiac arrest and analysis of its success factors[J].Chinese Journal of Clinicians, 2015,43(04):39-41.
[3]https://news.zhibo8.cc/zuqiu/2021-06-13/60c50dea4750b.htm.




























































You must log in to post a comment.